Variable Types
Logical variables
(boolean)
Logical type variables
can only have the value true (true) or false (false). They are often used in
control structures.
Note: The following example uses the if selection
structure that is explained in detail in the control structures lesson. To
understand this example, it is enough to know that if means if (if as a
condition, not yes as a statement) and is followed by a comparison of equality
== (comparisons are explained in the logical operations lesson). If the
comparison is true, that is, if the two terms on both sides of the comparison
are equal, the statement between brackets { } is executed.
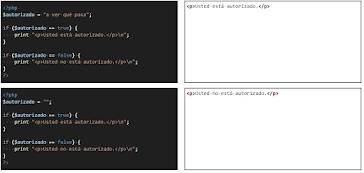
Note: It is not necessary to compare a logical variable
with true or false, we can use logical variables directly in the if condition.
Integer variables (integer)
Integer variables are
stored in computer memory using a fixed number of bytes, so you cannot store
arbitrarily large or small numbers. That number of bytes depends on the
architecture of the processor (32 or 64 bits), the operating system, and the PHP
version, but can be found using the predefined constant PHP_INT_SIZE). The
largest value that can be stored can be found using the predefined constant
PHP_INT_MAX.
If the result of an
integer calculation is too large to be represented by an integer, PHP
automatically converts it to decimal, losing precision.
Integers in
exponential, hexadecimal, octal, or binary notation
PHP allows you to
express integers in exponential, hexadecimal, binary, or octal notation.
The format of numbers
in exponential notation is mantisaeexponent which represents the number
mantissa * 10exponent. The mantissa can be an integer or a decimal and is
typically a value between 1 and 10, but the exponent must be an integer,
positive, or negative. So,
10000 would be written
as 1e4 (although it could also be written as 10e3, 100e2, etc.)
25000 would be written
as 2.5e4 (although it could also be written as 25e3, 250e2, etc.)
The format of numbers
in hexadecimal notation is 0xnumber. So,
255 would be written as
0xff
-256 would be written
as -0x100
The format of numbers
in binary notation is 0bnumber. So,
7 would be written as
0b111
-8 would be written as
-0b1000
The format of numbers
in octal notation is 0number. So,
255 would be written as
0377
-8 would be written as
-010
PHP allows operations
on numbers in any notation (each number can be in a different notation),
although the results are expressed in decimal notation.
Decimal variables
(float)
Decimal variables are
saved in all versions of PHP using the IEEE 754 64-bit format, so the maximum
value that can be saved or returned by calculation is 1.7976931348623E+308.
Decimal numbers in
exponential notation
PHP allows you to
express decimal numbers in exponential notation. The format of the numbers is
mantisaeexponent which represents the number mantissa * 10exponent. The
mantissa can be an integer or a decimal and is typically a value between 1 and
10, but the exponent must be an integer, positive, or negative. So,
-10000 would be written as 1e4 (although it could also
be written as 10e3, 100e2, etc.)
-25000 would be written as 2.5e4 (although it could
also be written as 25e3, 250e2, etc.)
-0.00045 would be written as 4.5e-4 (although it could
also be written as 45e-5, 450e-6, etc.)
String variables
(string)
String variables can
store characters.
PHP does not impose any
limits on the size of strings. Strings can be as long as server memory allows.
The character set used
by PHP is primarily determined by the character set used by the program's
source file. But keep in mind that the string handling functions are not
prepared to handle the diversity of character sets: many assume that each
character occupies only one byte, others assume a certain character set (UTF-8,
for example). , others use the locally defined charset, etc.
If a position greater
than the length of the string is specified, the string is lengthened with
spaces until it reaches that value:
Arrays
Arrays are covered in
the Arrays lesson.
Type conversions
PHP allows you to
convert variables of one type to another type or consider variables of one type
as another.
Variables as
logical variables
If an empty string is
considered a logical variable, it is considered to have the value false. If a
non-empty string is considered a logical variable, it is considered to have the
value true.
Non-empty strings are considered true, even if they have a value that might confuse us:
Arrays are always
considered true:











Comentarios
Publicar un comentario